Freak injuries in MMA
•••••••••••••••••••
Injuries are expected in combat sports, however on rare occasions freak injuries happen.
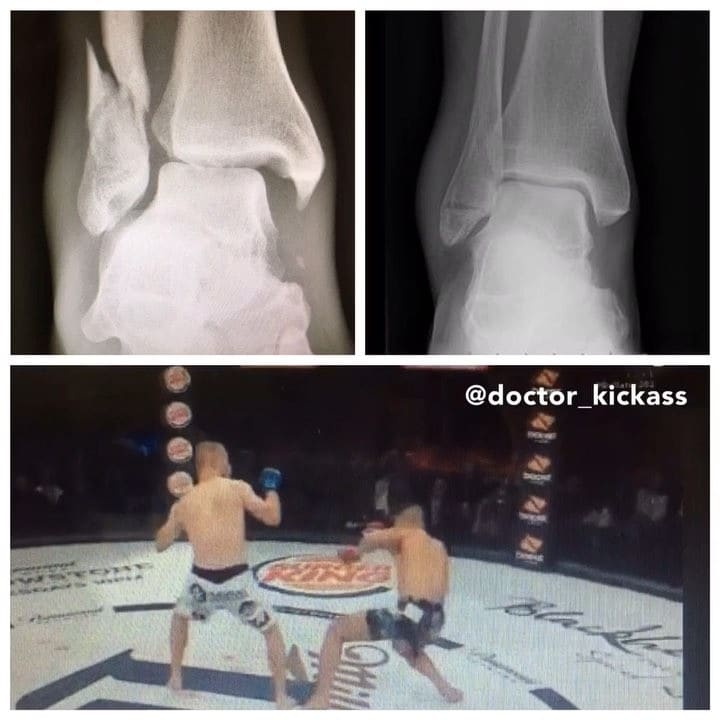
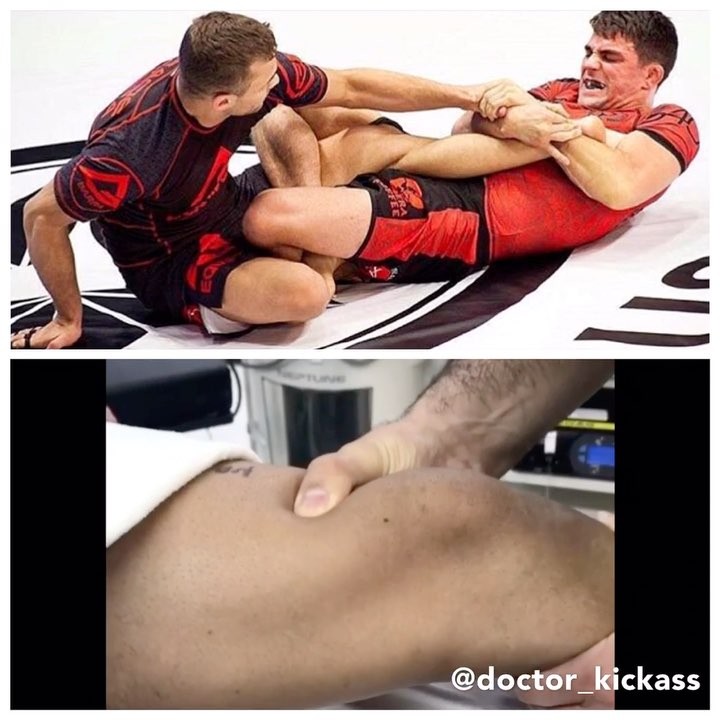
This weekend a freak injuries happened @bellatormma with MIchael McDonald vs Eduardo Dantas. MacDonald landed a punch that caused Dantas to stumble. In his attempt to remain balanced Dantas awkwardly landed on an everted ankle.
.
Dantas reported to @mmafightingdotcom that he suffered a fibula fracture and ankle ligament damage. These injuries require that he undergo surgery to address the fracture. Likely he will require open reduction internal fixation with a plate to realign the fibula for proper healing.
.
Despite the violent nature of fighting unfortunately injuries like this happen. Hopefully Dantas has a speedy recovery.
Biomechanics of the Armbar ••••••••••••••••• The armbar, arguably the most iconic technique in grapp
Biomechanics of the Armbar
•••••••••••••••••
The armbar, arguably the most iconic technique in grappling, is a submission that involves hyperextension of the elbow joint (humeroulnar joint). While there are two other joints around the elbow region:
1️⃣humeroradial
2️⃣radioulnar joint
.
the humeroulnar joint is the primary joint involved in elbow extension. After years of grappling many martial artists may lose a bit of range, but the average person should have about 5 degrees of hyperextension.
.
There are a variety of structures that limit hyperextension:
1️⃣muscle
2️⃣ligaments
3️⃣the bony articulation of the humerus and the ulna.
4️⃣The joint capsule is connective tissue that wraps around all three joints and is supported by ligamentous structures.
.
The primary ligament to limit excessive extension is the ulnar or medial collateral ligament (not to be confused with the MCL in the knee), particularly the anterior fibers which are the strongest and thickest fibers of the ligament. In addition to ligamentous support muscles of the elbow and forearm help to support and resist excessive motion, particularly the wrist flexors and pronators which act as dynamic medial stabilizers.
.
As the UCL is a fairly thick ligament and it is a highly innervated structure, the mechanoreceptors within the structure help detect passive tension. This is why there is a relatively moderate amount of time from when the submission begins and when damage occurs compared to a leg attack.
.
Humeroulnar hyperextension often leads to ligament strain of rupture, however if force is continued then dislocation of the ulna from the humerus can occur. While the muscles may become strained they are not likely to tear, more likely the muscle’s attachment on the ulna will rip off the main structure (avulsion fracture).
.
Here is an example of Keanu Subba demonstrating an armbar in @onechampionship . Initially Subba was unable to isolate the elbow due to his opponent wiggling his shoulder. Despite the arm being extended Subba could not impart enough force to disable the elbow. Once Subba had proper leg position he was able to isolate the elbow and elicit the tap.
Concussion Management: When to return to training ••••••••••••••••••• In combat sports where repeate
Concussion Management: When to return to training
•••••••••••••••••••
In combat sports where repeated head trauma is common, when is it safe to return to training?
.
Concussions are mild traumatic brain injuries that result from acceleration of the brain that creates a shearing force. This causes a metabolic energy crisis in the brain. The brain is vulnerable to worsening injury if further head trauma occurs.
.
When you no longer have symptoms you are cleared to train again, right? Symptoms may last for only 5 days but the metabolic energy crisis in the brain may last for up to 30 days. ✳️Even when you think you are fine your brain is still vulnerable❗️
.
How do I know when it is safe to return? Here is a recommended guideline on when to return. (Zurich consensus statement 2013)
1️⃣Symptoms resolution
2️⃣Neurological assessment return to baseline
•Cranial Nerve normal •Balance normal •Vestibular Ocular Reflex normal
3️⃣Neurocognitive assessment return to baseline
4️⃣Graduated physical exertion
.
Get cleared by a medical professional trained in concussion management before returning to training / competition❗️
As a martial artist I understand wanting to return to training ASAP but without adequate recovery it is possible for symptoms to become chronic and linger.
.
I would recommend professional MMA fighters to get a baseline neurological / neurocognitive assessment prior to competition to accurately determine a safe time to return.
.
Reference:
1️⃣McCrory, P., Meeuwisse, W. H., Aubry, M., Cantu, B., Dvořák, J., Echemendia, R. J., … & Sills, A. (2013). Consensus statement on concussion in sport: the 4th International Conference on Concussion in Sport held in Zurich, November 2012. Br J Sports Med, 47(5), 250-258.
Patellar CARs: Knee cap health ••••••••••••••• Controlled articular rotations generally involve ACTI
Patellar CARs: Knee cap health
•••••••••••••••
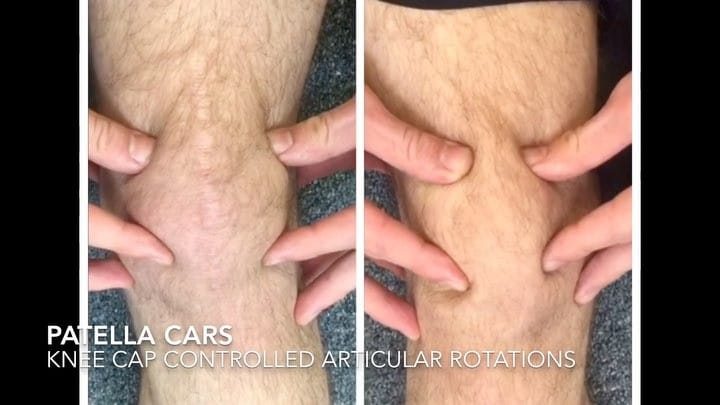
Controlled articular rotations generally involve ACTIVE movement, however one joint that will benefit from passive movement is the patella. .
Why is movement important for knee health?
✅Movement and load are how the knee cap repairs itself.
.
Between the knee cap (patella) and the leg (femur) is articular cartilage, which allows for smooth motion between the two bones. Unfortunately unlike other structures in the body there is no blood supply, meaning articular cartilage has a limited ability to heal or repair itself. .
If the ability to repair itself is limited then what can you do to help the process?
.
“Joint motion and load are important to maintain normal articular cartilage structure and function. Inactivity of the joint has also been shown to lead to the degradation of cartilage. Regular joint movement and dynamic load is important for the maintenance of healthy articular cartilage metabolism. The development of disease such as osteoarthritis is associated with dramatic changes in cartilage metabolism. This occurs when there is a physiological imbalance of degradation and synthesis by chondrocytes. (Fox 2009)”
.
Patellar mobility is essential for general knee health however for activities like Jiu jitsu it is extremely important. In Jiu jitsu often excessive weight bearing occurs through kneeling which forces a lot of practitioners to wear knee pads to reduce the load. Gentle joint movement helps reduce wear and tear.
.
Learn how to take care of your body!
.
Reference:
Sophia Fox, A. J., Bedi, A., & Rodeo, S. A. (2009). The basic science of articular cartilage: structure, composition, and function. Sports health, 1(6), 461-468.
.
@functionalrangerelease @functionalrangeconditioning @drmchivers @drandreospina
How to train your grip for jiu jitsu •••••••••••••••••••••••• In all grappling arts the one who is a
How to train your grip for jiu jitsu
••••••••••••••••••••••••
In all grappling arts the one who is able to establish their control has a significant advantage over their opponent. Grappling arts involving a kimono (jiu jitsu, judo, sambo etc..) often involve heavy grip fighting or kumi kata in japanese.
.
While the grip battle is important just how important is it?
.
One study found that the forearm and fingers were the two primary muscle groups to fatigue in a jiu jitsu match compared to all other muscle groups (Andreato 2017). The researcher also noticed that by the end of a 10 minute simulation the maximal handgrip strength decreased 89/84% from baseline (dominant, non dominant respectively) (Andreato 2013). The drop in maximal grip strength was noticed by the 4th minute in the match and remained significantly lower than baseline until the end of the match
.
While grip strength and endurance is not the only attribute (physical or technical) that is necessary for success in kimono grappling competition it is not one that should be overlooked.
.
Here are 3 exercises that you can use to train your grip strength:
•Farmer’s Carries: Any carry or deadlift variation is great for grip and general strength.
•Slow towel pullups: Great for building muscular endurance,
•Grip trainers: Isolating grip trainers if your grip is a limiting factor.
.
References:
1️⃣Andreato, L. V., Esteves, J. V. D. C., Julio, U. F., Panissa, V. L. G., Hardt, F., de Moraes, S. M. F., & Franchini, E. (2017). Physical performance, time-motion, technical-tactical analyses, and perceptual responses in Brazilian jiu-jitsu matches of varied duration. Kinesiology, 49(1).
2️⃣Franchini, E., Artioli, G.G., & Brito, C.J. (2013). Judo combat: Time-motion analysis and physiology. International
Journal of Performance Analysis in Sport , 13 (3), 624-641.
3️⃣Andreato, L.V., Franchini, E., Franzói-Moraes, S.M., Pastório, J.J., Silva, D.F., Esteves, J.V.D.C., Branco, B.H.M.,
Romero, P.V.S., & Machado, F.A. (2013). Physiological and technical-tactical analysis in Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu
competition. Asian Journal of Sports Medicine , 4 (2), 137-143.
Hamstring strain rehab ••••••••••••••••••• A “pulled” hamstring is a strain to the muscle of varying
Hamstring strain rehab
•••••••••••••••••••
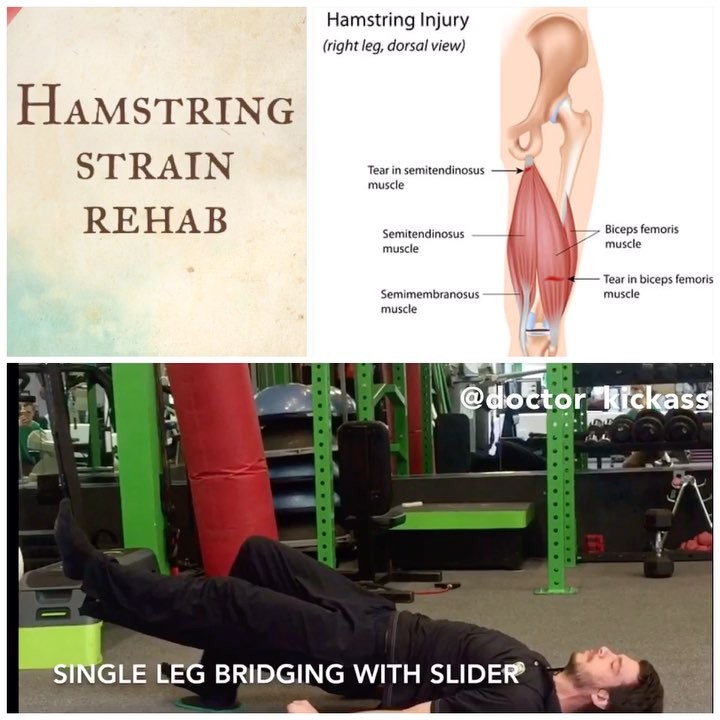
A “pulled” hamstring is a strain to the muscle of varying degrees. Hamstrings, the big muscles on the back of your thigh, are often injured in high energy athletic movements (running, jumping, kicking etc…). The hamstrings are a group of 3 muscles that cross the knee and hip:
* Semitendinosus.
* Semimembranosus.
* Biceps femoris (which includes a short head and long head)
Cause of strain:
Muscle strains occur due to overloading, meaning the muscle could not control the force of the required movement. .
Rehab strategies: Once you are diagnosed with a hamstring strain, how do you fix it? Strength the specific injured area and strengthen the whole muscle group. .
Phase I: Early strategies
1️⃣Gentle pain-free movement: walking, biking, swimming. Anything moving that does not hurt.
2️⃣Positional isometrics: Gradually slide your heel away from you and every 10 degrees test how it feels to contract your hamstrings. If there is a specific point that is painful then back off and start isometrically loading that area. Isometrics initiate the specific strengthening of the injured tissue and helps to reduce pain.
Phase II
3️⃣Bridging: When the pain from hamstring contraction lessens this is an intermediate loading strategy. The further your feet are away the more taxing it is for your hamstring.
4️⃣Bridging with slider: As pain continues to reduce a progress exercise involves slow eccentric loading of the hamstring. Only move your foot as far as you can control without pain.
Phase III: Advanced Strategies
5️⃣Single leg bridging with slider: Before returning to competition it is important that the injured leg can handle larger loads without assistance from the healthy hamstring.
.
Make sure to see a healthcare professional to diagnose and treat your injury so it does not become a lingering problem.
Biomechanics of the Armbar ••••••••••••••••• The armbar, arguably the most iconic technique in grapp
Biomechanics of the Armbar
•••••••••••••••••
The armbar, arguably the most iconic technique in grappling, is a submission that involves hyperextension of the elbow joint (humeroulnar joint). While there are two other joints around the elbow region:
1️⃣humeroradial
2️⃣radioulnar joint
.
the humeroulnar joint is the primary joint involved in elbow extension. After years of grappling many martial artists may lose a bit of range, but the average person should have about 5 degrees of hyperextension.
.
There are a variety of structures that limit hyperextension:
1️⃣muscle
2️⃣ligaments
3️⃣the bony articulation of the humerus and the ulna.
4️⃣The joint capsule is connective tissue that wraps around all three joints and is supported by ligamentous structures.
.
The primary ligament to limit excessive extension is the ulnar or medial collateral ligament (not to be confused with the MCL in the knee), particularly the anterior fibers which are the strongest and thickest fibers of the ligament. In addition to ligamentous support muscles of the elbow and forearm help to support and resist excessive motion, particularly the wrist flexors and pronators which act as dynamic medial stabilizers.
.
As the UCL is a fairly thick ligament and it is a highly innervated structure, the mechanoreceptors within the structure help detect passive tension. This is why there is a relatively moderate amount of time from when the submission begins and when damage occurs compared to a leg attack.
.
Humeroulnar hyperextension often leads to ligament strain of rupture, however if force is continued then dislocation of the ulna from the humerus can occur. While the muscles may become strained they are not likely to tear, more likely the muscle’s attachment on the ulna will rip off the main structure (avulsion fracture).
How to strengthen the rotator cuff: Basic introduction to strengthening the shoulder •••••••••••••••
How to strengthen the rotator cuff: Basic introduction to strengthening the shoulder
••••••••••••••••••••
A stable shoulder will have the humeral head centered in the glenoid fossa with arm movements. When someone has a defective rotator cuff or “loose” static stabilizers they may lack the ability to keep the shoulder stable with movement. Inability to maintain stability is often the cause of shoulder pain.
.
Shoulder pathology that may benefit from rotator cuff strengthening:
1️⃣shoulder impingement
2️⃣rotator cuff strains/tears
3️⃣labral tears / shoulder instability
.
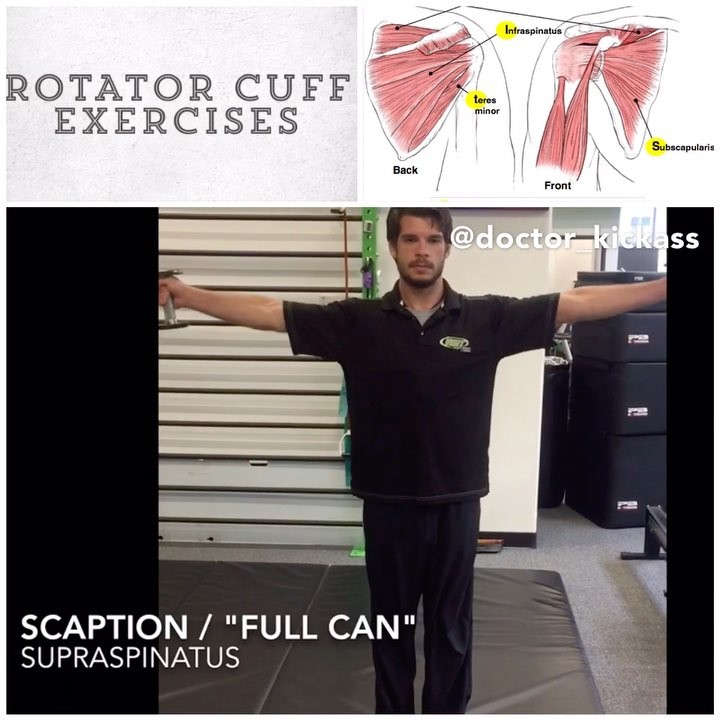
Rotator cuff muscles (Dynamic stabilizers): The rotator cuff is a collection of 4 muscles that act like suction cups on the humeral head to keep it compressed and stable.
1️⃣Supraspinatus
2️⃣Subscapularis
3️⃣Infraspinatus
4️⃣Teres minor
Here are 3 exercises that are excellent basic / initial exercises to strengthen the rotator cuff: Each of these three exercises have high levels of muscle activation for at least one specific rotator cuff muscle.
1️⃣Push up plus: Typically this exercise is used for serratus anterior strengthening, however it also has shown to be a strong activator of the subscapularis.
2️⃣Scaption / “Full Can”: This exercise has high activation of the supraspinatus with less potential complications compared to similar rotator cuff exercises, such as the empty can.
3️⃣Sidelying Shoulder External Rotation: This exercise, moving a resistance against gravity, has high activation of both the infraspinatus and teres minor. The sidelying position tends to get better activation of the shoulder external rotators than other variations of similar exercises.
.
References:
1️⃣Wilk, K. E., Reinold, M. M., & Andrews, J. R. (2009). The athlete’s shoulder. Elsevier Health Sciences.
2️⃣Escamilla, R. F., Yamashiro, K., Paulos, L., & Andrews, J. R. (2009). Shoulder muscle activity and function in common shoulder rehabilitation exercises. Sports medicine, 39(8), 663-685.
Got sciatica? ••••••••••••••••••• Sciatica is an overused term to describe what people feel when the
Got sciatica?
•••••••••••••••••••
Sciatica is an overused term to describe what people feel when they get shooting pain down their legs. Nerve pain can either be due to nerve root compression or peripheral nerve entrapment (often sciatica). Let a healthcare professional diagnose the problem but here is a strategy to address the problem.
.
What to do?
1️⃣Find your pain trigger: bend forward, bend backward, bend to the side and rotate. This lets you know what motions cause more nerve pain or pain that moves further down your legs.
2️⃣Commonly a trigger for worsening symptoms occurs with forward bending. If this is the cause a common intervention that can reduce symptoms is the opposite direction: extension/backward bending.
3️⃣Exercise: The prone cobra / prone press up. Maintaining a position of being on your elbows or hands (whatever you can tolerate). Often rapid repeated floppy push ups may irritate the spinal facets so perform 10×10 second holds and re-assess for any changes. ❗️If symptoms worsen or progress STOP. If you notice a change keep performing until symptoms plateau. .
‼️Do not panic and rush for a MRI. As a healthcare professional I don’t treat that the images shows, I treat what I find. People often have worse prognosis after hearing the results of imaging because it makes them feel ‘damaged’. The problem is just because the images show a defect it does not mean it is the cause of pain. .
✅Make sure to see a healthcare professional who can confirm the diagnosis and address any contributing factors to your symptoms.
ACL insufficiency •••••••••••••••••••••• With the popularity of leg locks in modern grappling, such
ACL insufficiency
••••••••••••••••••••••
With the popularity of leg locks in modern grappling, such as heel hooks, there is a higher likelihood of ligamentous injury. .
Lachman’s test: This is an orthopedic test used to assess the integrity of the anterior crucial ligament (ACL). The ACL’s primary role is to resist anterior translation, especially at 20-30 degrees of knee .
Lachman Statistics: 84.6% sensitivity and >95% specificity. High specificity means it is excellent test to rule in ACL damage. .
Note for non-clinicians: Clinicians make diagnosis with a variety of data, one test is not the only way to rule in our rule out an injury.
.
Video footage credit: @drnimamehran
Forearm fracture with improper punch •••••••••••••••••• The forearm is actually composed of two bone
Forearm fracture with improper punch
••••••••••••••••••
The forearm is actually composed of two bones: radius and ulna. The two bones have an articulation proximal, distal plus an interossus membrane. Th membrane which allows force distribution between the bones to unload excessive force, particularly with axial or weight bearing force.
.
Despite the anatomical features to allow for a deload of axial force the bones were not designed to resist significant shear force, such as blunt force trauma. .
In this example Artem Damkovsky threw a circular punch however due to misjudging the distance with his strike he landed on his lateral forearm bone instead of his fist. The fighter was unable to continue the fight and it was determined he suffered a forearm fracture.
.
Important note❗️It was not disclosed which bone was fractured however based on the site of impact I would hypothesis that he fractured his radius. Certainly possible he could have broken both the ulna and radius.
.
Injuries happen in fighting however this demonstrates the importance of proper distance management so you do not inflict more damage to yourself than your opponent.
.
@m1global
BJJ warm up: Perspective from a physical therapist •••••••••••••••••••••• Warming up properly is ess
BJJ warm up: Perspective from a physical therapist ••••••••••••••••••••••
Warming up properly is essential for martial artists because these activities are fairly strenuous with a decent risk for injury. Unfortunately in my opinion most warm ups for jiu jitsu are a WASTE of precious TIME that can be devoted to learning and training the art.
.
What’s the point of a warm-up? The goal of a warm-up is to physically prepare the athlete/martial artist for an immediate bout of training or competition.
Physiological responses to a warm-up:
1️⃣Raise core body and muscle temperature
2️⃣Decrease joint fluid viscosity
3️⃣Enhance metabolic flow
4️⃣Increase blood flow to muscles
5️⃣Improve oxygen delivery
.
Based on this information how can you best prepare your body for jiu jitsu as efficiently as possible?
.
Global controlled articular rotations (CARs): Taking each joint through their full available pain-free motion. Adding irradiation, gradually increasing tension, through these motions to prepare each joint for every range of motion that is required for jiu jitsu. Generally before a workout you can use a moderate or 50% contraction for optimal joint preparation.
.
This video is sped up but doing a CAR for each joint in the body with proper tension should take 4-5 minutes. Repeat for any joint that requires attention.
.
@functionalrangeconditioning @functionalrangerelease @kinstretch @drandreospina @drmchivers @dynamixmma
Simply explanation to improve success with throws for jiu jitsu. Jiu jitsu players understand the co
Simply explanation to improve success with throws for jiu jitsu. Jiu jitsu players understand the concept of kuzushi on the ground but fail to apply these same concepts while on the feet.
#Repost @davecamarillo with @get_repost
・・・
O Goshi // Judo Throws require the proper execution and timing of Kuzushi (The Destruction of an opponent’s base) to lower the chance of being countered. Many Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu Practitioners do not learn proper off-balancing when they use Judo in their training. This will have a debilitating effect for the practitioner. It will also increase the leverage of their opponent creating a false sense of security. The hip throws of judo are dynamic, thus pleasing to the eye. What is not pleasing or desirable is the improper execution of these throws. Functionality should always take the place of marketability. Create proper habits with proper training and reap the rewards…
Intermediate lumbar stability exercises ••••••••••••••••••• 1& pressure breathing (IAP): Using breat
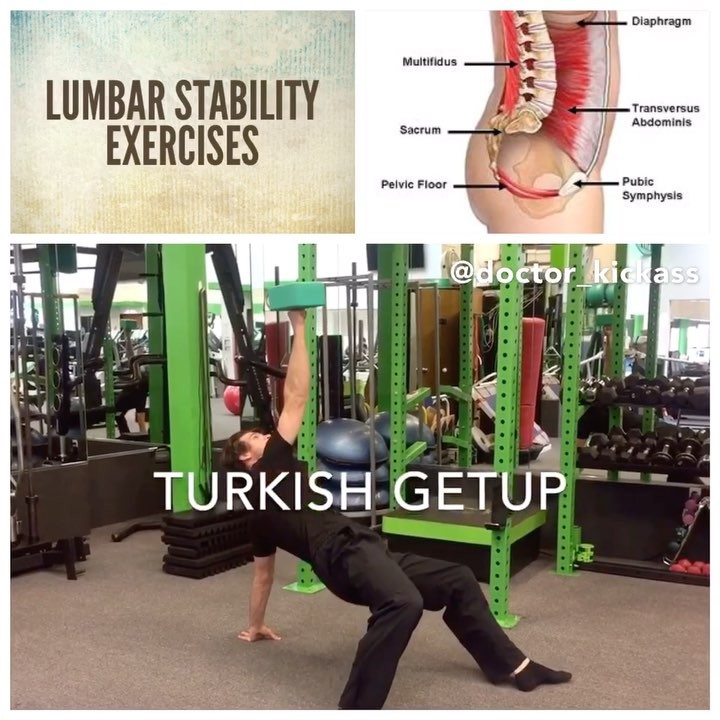
Intermediate lumbar stability exercises
•••••••••••••••••••
1️⃣Intra-abdominal pressure breathing (IAP): Using breathing to help stabilize the lumbar spine. You should feel expansion in your belly and low back and not expansion of the chest.
2️⃣Lumbar isometric holds: abdominal bracing in multiple planes.
3️⃣Isometric abdominal stiffness with distal movements: chopping motion where the arms move and the spine remains stiff.
4️⃣Turkish getup: remaining stable in a variety of positions. Lightweight box forces slowed controlled motion and lock in each transition.