Physiology of a liver strike
•••••••••••••••••••••••••
In combat sports fighters often focus on aiming for the head to finish the fight however one effective alternative is one that targets the liver. The liver is an organ that sits in the right abdominal cavity immediately behind the lowest ribs. While the ribcage does a good job of protecting many vital organs the liver remains partially uncovered and can be prone to attack. Traumatic impact to the liver, via punch, kick or knee can be excruciatingly painful and can incapacitate your opponent.
.
How can a liver strike cause this effect? .
Vasovagal syncope. The vagus nerve innervates many vital organs and connects the parasympathetic nervous system or “rest and digest” system. As the liver is one of the few organs left unprotected by the ribs when it is struck with a sufficient force it can unbalance the parasympathetic nervous system. When the system is stimulated in this manner there can be a cardioinhibitory (slows heart rate) and/or vasodepressor response (blood pressure drops). When this happens there is reduced blood flow to the brain, which can cause fainting, confusion or temporary paralysis. People often describe this feeling as their bodies turn off momentarily.
.
In boxing a liver shot is often when an orthodox fighter throws a left hook to the body against an opponent with a staggered stance. In kickboxing or muay thai this is often when a southpaw fighter throws a rear leg body kick to an opponent with a mirror stance or open stance.
.
Many strikers focus their efforts on the head but the body has many other weak points that can be exploited to win the fight.
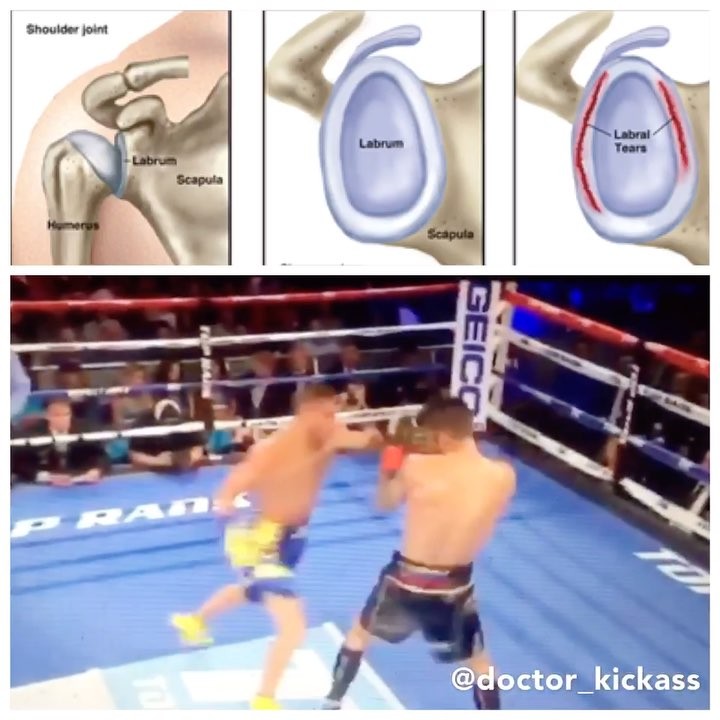
Labral tears and combat sports •••••••••••••••••• The shoulder has the most mobil
Labral tears and combat sports
••••••••••••••••••
The shoulder has the most mobility of any joint, and unfortunately the more mobility a joint has the less inherent stability there is.
.
The shoulder (glenohumeral joint) involves the head of the humerus (upper arm) articulating with the glenoid fossa.
•A stable shoulder will have the humeral head centered in the glenoid fossa with arm movements.
•An unstable shoulder means the dynamic and static stabilizers are unable to keep the humeral head centered.
1️⃣Dynamic stabilizers (rotator cuff muscles): These muscles act like suction cups on the humeral head to keep it compressed and stable.
2️⃣Static Stabilizers: ligaments, joint capsule and labrum.
Glenoid labrum: The function of the glenoid labrum is to deepen the socket for the humeral head so that it has more contact with the fossa
Shoulder dislocations: When the stabilizers fail and the humeral head translates too far from the fossa. The most common dislocation is anterior (forward). The static stabilizers often gets damaged or torn so repeated dislocations are common after the first.
Why does the labrum get damaged in fighting?
Biceps brachii is an arm muscle with two heads, and the long head of the biceps has significant attachment to the superior aspect of the labrum (up to 50%). Due to the strong connection with the labrum when there are large or repetitive forces on or from the biceps load will be transferred to the labrum. This occurs in combat sports with repetitive maximal punches.
.
An example of this was Lomachenko vs Linares. When @lomachenkovasiliy throws the lead hook it appears that his shoulder translates too far forward (anterior dislocation) and he relocates it with the excessive swing back. Following the fight it was revealed Lomachenko had a severe labrum tear and significant instability. Some labrum tears may respond to conservative treatment but in his case surgery was required.
.
References:
1️⃣Neumann, D. A. (2010). Kinesiology of the musculoskeletal system: Foundations for rehabilitation. 2. p. Mosby Elsevier.
2️⃣Wilk, K. E., Reinold, M. M., & Andrews, J. R. (2009). The athlete’s shoulder. Elsevier Health Sciences.
One exercise to treat achilles tendonitis
Achilles tendonitis, calf, and heel pain can really limit your function and ability to perform a deep squat while exercising or even get into proper position in BJJ such as being on active toes when in an opponent’s guard. This exercise using an eccentric contraction (“negatives”) to not only actively stretch the calf and foot, but to also strengthen the calf muscle in a pain-free way can really be effective.
Instagram: the_jiujitsu_therapist
Facebook: www.facebook.com/jiujitsuPT
Twitter: jiujitsuPT
Falling and elbow injuries •••••••••••••••••••• The skill of falling properly is
Falling and elbow injuries
••••••••••••••••••••
The skill of falling properly is one of the most important techniques that a grappler can learn. Falling properly minimizes potential injuries to the head, neck, shoulder, elbow and wrist. Unfortunately even accomplished grapplers and fighters may land incorrectly while in the middle of a competition or fight. .
Elbow injuries usually occur when the grappler reaches out to post on an outstretched arm. The elbow often is the weakest link and the source of injury.
.
There are a variety of structures that limit hyperextension:
1️⃣muscle
2️⃣ligaments
3️⃣the bony articulation of the humerus and the ulna.
4️⃣The joint capsule is connective tissue that wraps around all three joints and is supported by ligamentous structures.
The primary ligament to limit excessive extension is the ulnar or medial collateral ligament (not to be confused with the MCL in the knee), particularly the anterior fibers which are the strongest and thickest fibers of the ligament. In addition to ligamentous support muscles of the elbow and forearm help to support and resist excessive motion, particularly the wrist flexors and pronators which act as dynamic medial stabilizers.
.
Humeroulnar hyperextension often leads to ligament strain of rupture, however if force is continued then dislocation of the ulna from the humerus can occur. While the muscles may become strained they are not likely to tear, more likely the muscle’s attachment on the ulna will rip off the main structure (avulsion fracture).
.
Continue to practice breakfalls to minimize the risk for freak elbow injuries from occurring.
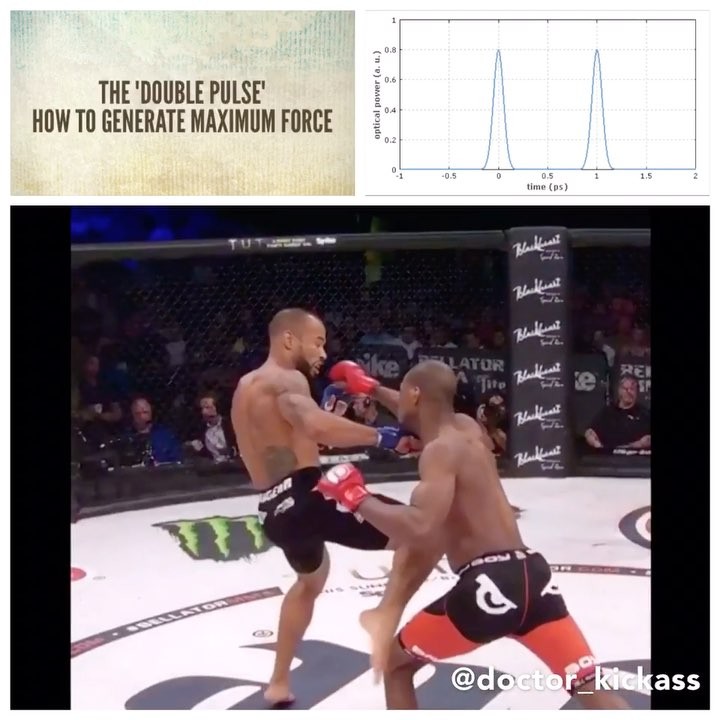
The “Double Pulse”: How to generate maximum force ••••••••••••••••••••••••• In st
The “Double Pulse”: How to generate maximum force
•••••••••••••••••••••••••
In striking martial arts the ultimate goal is to generate power sufficient enough to render an opponent unconscious. How can one generate enough force to accomplish this task?
.
In terms of striking muscle contract to initiate the strike and create force, however a maintained contraction will slow the strike. To generate maximal force one has to contract to generate the movement and immediately relax to minimize ‘stiffness” during the follow through. Immediately before contact the contraction occurs again to create maximum force. Dr. Stu McGill refers to this as the “double pulse”.
.
McGill discovered that fighters who generate the most force are ones who have a high rate of contraction AND a high rate of relaxation. “The rate of muscle contraction, and the rate of relaxation, determines the strike speed and impact force. -Dr. Stu McGill
.
A good example of the double pulse, is @michaelvenompage ‘s knockout at @bellatormma . Page is an excellent example of a fighter who can generate power and relax at an alarmingly high rate.
.
Reference:
McGill, S.M., Chaimberg, J., Frost, D., Fenwick, C. (2010) The double peak: How elite MMA fighters develop speed and strike force. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. 24(2): 348-357.
How to maximally stress the MCL ••••••••••••••••••••• Here @eddie_wolverine demon
How to maximally stress the MCL
•••••••••••••••••••••
Here @eddie_wolverine demonstrates a mean sideways kneebar variation. Unlike a classic kneebar this leg lock isolates the knee ligament, medial collateral ligament. In addition to isolating the ligament there is not additional support from the bony articulation because the knee is slightly bent. This joint lock looks very similar to an orthopedic test used to assess for the integrity of the medial collateral ligament, the valgus stress test.
.
Steps to maximize the breaking force on this leg lock variation.
1️⃣ Slight bend in the knee to unlock the bony articulation of the femur and tibia.
2️⃣Externally rotate the tibia to put the MCL on stretch.
3️⃣Impart a valgus force to maximally stress the ligament. .
I would recommend caution when applying this leg lock variation to give your opponent ample time to tap before their knee ligament is ruptured.
Which grappler doesn’t have tight hip flexors!?
Want to see Sebastian channel his inner Michael Jackson? You’re in the right spot!
When you’re done laughing, continue with the video – you will stretch your quads and give your hip flexors a bit of a break.
These are the poses we never do in jiu jitsu, but it’s so essential to counter all the movements from training.
If you feel any kind of pain while doing this, use the modifications showed/mentioned by Sebastian! If it still hurts, please go to https://www.yogaforbjj.net and contact us! We’ll be able to give you more guidance and tips.
Good training is fuelled by good nutrition. My favourite ‘cheat’ meal.
Good training is fuelled by good nutrition. My favourite ‘cheat’ meal.
– peel & boil potatoes for 10 min. Mash with some coconut oil – beat eggs
– mix in nuts and seeds
– mix in potatoes
– cook on a good non stick pan
– top with berries
#glutenfree #breakfast #bjj via @RiplApp
2018-05-20 13:36:31
How To Fix Thoracic Spine and Rib Tightness
I received a question on Reddit asking about how to alleviate recurrent rib injuries and muscle pulls from BJJ. The intercostal muscles (muscle between the ribs) are constantly in motion as they allow for the ribs to expand and contract with breathing and help with some stability between the ribs. These muscle can get irritated and then have a tedency to be re-irritated frequently. A dynamic warm up to help with blood flow and allow the muscles to get some light and comfortable movement will assist with reducing tightness, pain, and getting the area generally primed for more vigorous activity. Try these 4 quick exercises/warm-ups to get your body set to train.
Instagram: the_jiujitsu_therapist
Facebook: www.facebook.com/jiujitsuPT
Twitter: jiujitsuPT
How To Fix Thoracic Spine and Rib Tightness
I received a question on Reddit asking about how to alleviate recurrent rib injuries and muscle pulls from BJJ. The intercostal muscles (muscle between the ribs) are constantly in motion as they allow for the ribs to expand and contract with breathing and help with some stability between the ribs. These muscle can get irritated and then have a tedency to be re-irritated frequently. A dynamic warm up to help with blood flow and allow the muscles to get some light and comfortable movement will assist with reducing tightness, pain, and getting the area generally primed for more vigorous activity. Try these 4 quick exercises/warm-ups to get your body set to train.
Instagram: the_jiujitsu_therapist
Facebook: www.facebook.com/jiujitsuPT
Twitter: jiujitsuPT
Join our Private Facebook Group
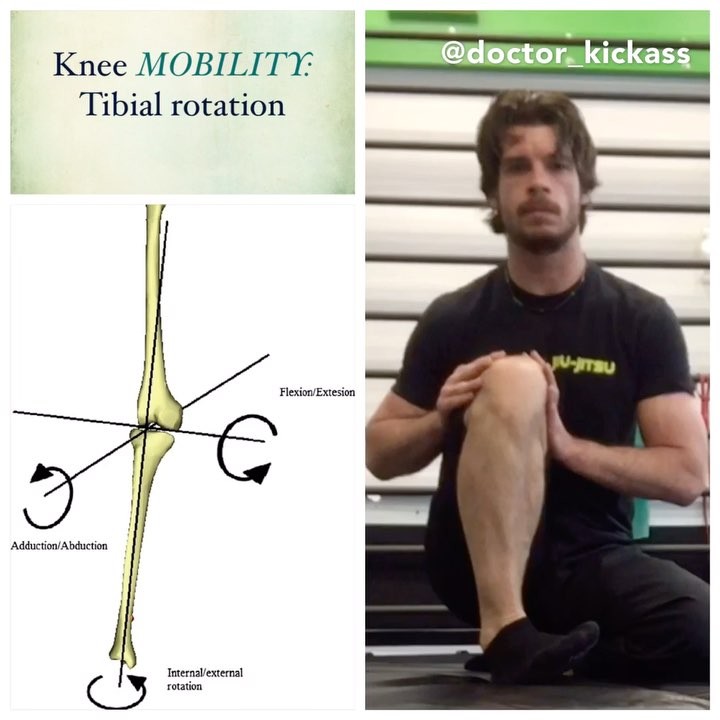
How well does your knee rotate? ••••••••••••• As a clinician a very common findin
How well does your knee rotate?
•••••••••••••
As a clinician a very common finding I see is patients who are unable to actively rotate their knee (even when they are not coming to see me for a knee injury).
.
The tibiofemoral joint (knee) has 2 degree of freedom:
1️⃣bends and straightens (flexion, extension).
2️⃣shin spinning inside and outside (tibial internal and external rotation on the femur). There is a 2:1 ratio of external rotation to internal rotation, where the most rotation occurs when the knee is flexed to 90 degrees. Often clinicians focus on improving linear movement however introducing rotational movement can also improve global knee function.
.
How do you improve your ability to rotate your tibia on your femur?
•Regressed knee controlled articular rotation: Since rotation is greatest at 90 degrees of flexion this is the best place to teach someone the movement. ✅Important tip: Drive your heel into the floor and keep your toes hovering over the ground. This helps to create irradiation for maximal motor activation plus minimizes compensatory ankle movement that often creates the illusion of the tibia spinning.
.
@functionalrangeconditioning @functionalrangerelease @drandreospina @vertfit
Treating the hip capsule with functional release techniques ••••••••••••• After a
Treating the hip capsule with functional release techniques •••••••••••••
After a thorough assessment it was apparent the patient had poor hip mobility and extensibility. This was his second treatment, initially his right hip had 0 degrees of hip internal rotation.
.
Functional release treatment to the hip joint capsule:
1️⃣Anterior hip: pectineus, obturator externus
2️⃣Posterior hip: piriformis, gemelli and obturator internus.
.
The “release” mechanism involves:
1️⃣extrinsic forces: manual input with directional force on fibrotic aspects of the hip capsule.
2️⃣progressive angular isometric loading: the patient’s intrinsic isometric holds.
.
Manual treatment was followed up with FRC mobility exercises: high tension controlled articular rotations and higher tension progressive angular isometric loading / regressive angular isometric loading to lock in those improvements. .
@functionalrangerelease @functionalrangeconditioning @drmchivers @drandreospina @vertfit
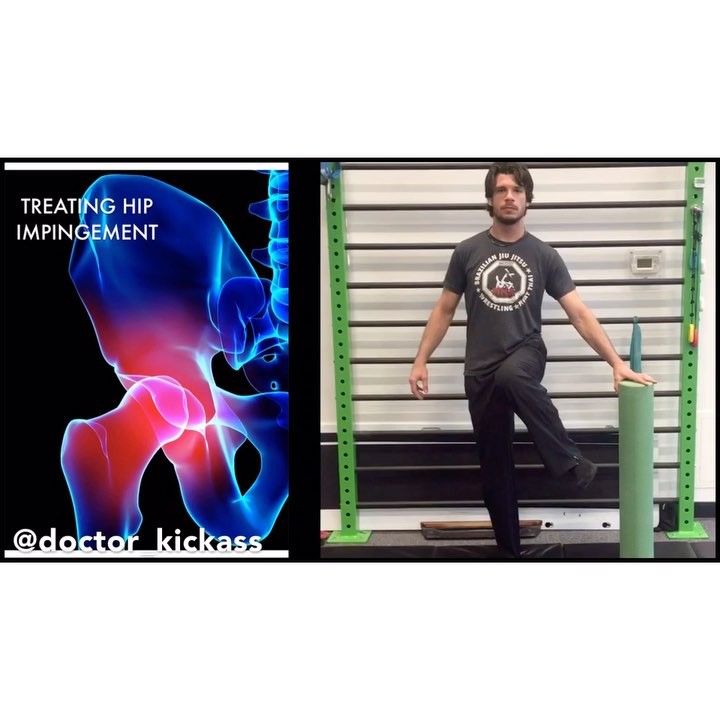
Hip impingement rehab ••••••••••••••••••• Hip impingement or femoroacetabular imp
Hip impingement rehab
•••••••••••••••••••
Hip impingement or femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is a term to describe abnormal contact with the femur and the acetabulum. If left untreated this can cause irritation and result in degenerative changes to the hip. Often this is due to anatomical variance but also this may be due to capsular tightness and poor hip motor control.
.
Impingement sign: The hallmark sign is pain with end-range flexion and internal rotation. This is a closing angle dysfunction.
.
Rehab options using FRC concepts:
1️⃣Hip 90/90 Stretch + PAIL/RAIL to reduce passive restrictions and initiate end-range motor control.
2️⃣Hip Internal rotation lift off: This is a safe position to improve hip internal rotation mobility without working in aggravating ranges of motion.
3️⃣Hip controlled articular rotations: Focus on hip rotation control.
.
Additional options may include Functional release manual techniques to the deep posterior hip capsule.
.
Those with anatomical variance may require surgical intervention but I would recommend exploring conservative treatment first.
.
@functionalrangeconditioning @functionalrangerelease @drandreospina @drmchivers @kinstretch
Ultimate rehab programs for grapplers, BJJ athletes and MMA fighters
Are you currently injured, or always dealing with an older injury?
You probably know we think yoga is great, but sometimes you need something more specific to rehab that injury.
We recently uploaded a bunch of rehab programs on https://www.yogaforbjj.net
Currently available are: elbow, knee, shoulder, neck and ankle rehab programs
Coming soon: lower back and hamstrings injury rehab programs
Created by Rosi Sexton – our expert that understands BJJ injuries and how to treat them better than pretty much anyone. She’s a BJJ brown belt, WMMA pioneer and an osteopath with her own practice.
Ready to start working on being injury free?
https://www.yogaforbjj.net/programs